When considering car maintenance responsibilities, understanding the intricacies of warranties is essential. One common question car owners face is whether a timing belt is covered under warranty. This component is crucial for engine function, and knowing its warranty status can save you from unexpected repair costs.
What is a Timing Belt?
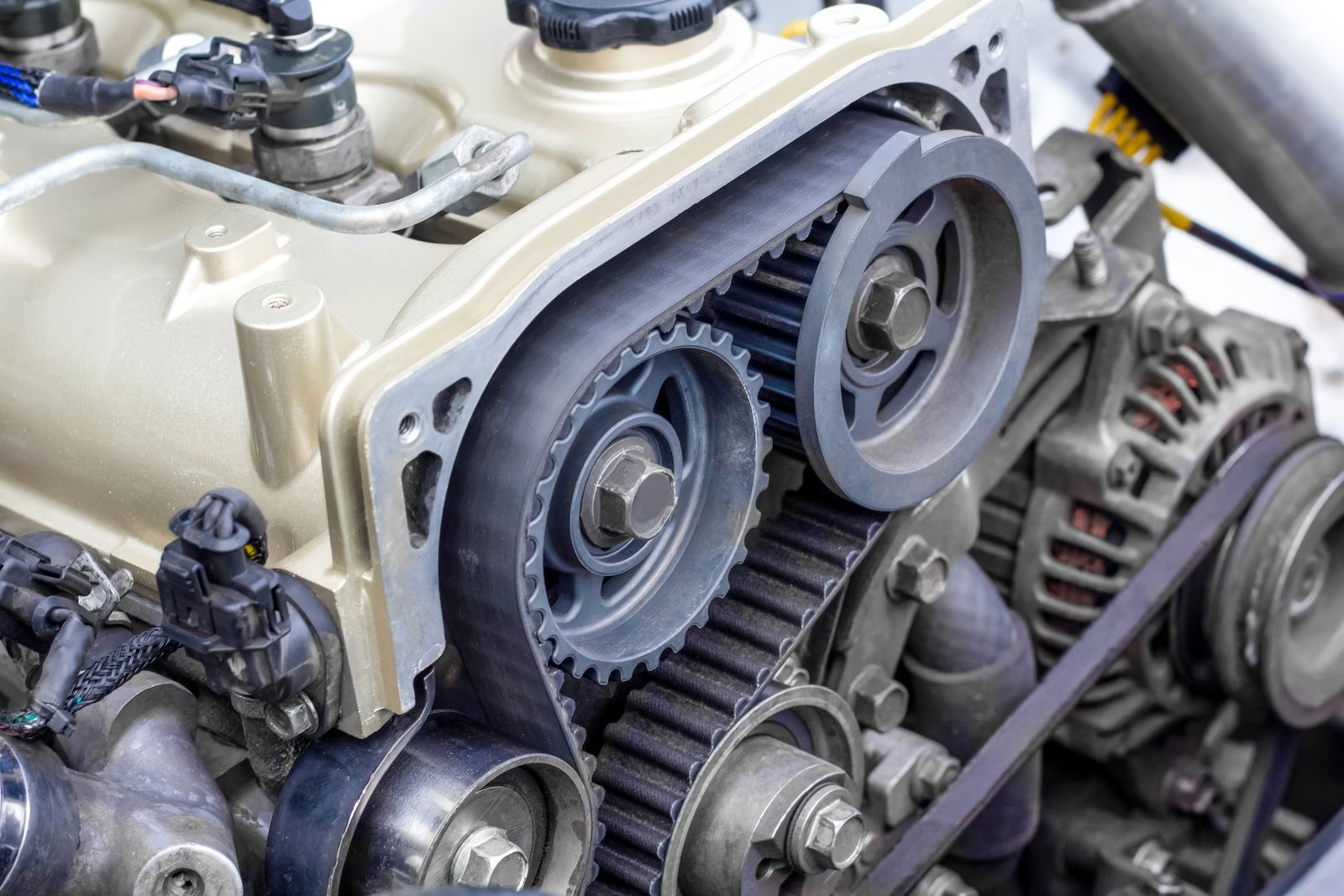
The timing belt is an integral part of an internal combustion engine. It connects the engine’s crankshaft to the camshaft, ensuring that the engine’s valves open and close in synchronization with the position of the pistons. A well-functioning timing belt is essential for optimal engine performance, and a failure can lead to severe engine damage.
Most vehicles have specific intervals for timing belt replacements, usually every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the vehicle manufacturer. However, the timing belt can sometimes fail prematurely due to a variety of factors, including manufacturing defects, improper installation, or insufficient maintenance.
Understanding Vehicle Warranties
Vehicle warranties are protection plans that manufacturers offer to cover certain repairs and parts of your vehicle for a specified period or mileage. Generally, there are two main types of warranties: the basic (or bumper-to-bumper) warranty and the powertrain warranty.
The basic warranty covers most repairs needed on your vehicle during the initial period. This includes various parts and systems, but certain exclusions often apply. On the other hand, the powertrain warranty focuses on the engine, transmission, and drivetrain components.
Is a Timing Belt Covered Under Warranty?
Whether a timing belt is covered under warranty usually depends on the specifics of the warranty itself. Most standard warranties typically do not cover wear-and-tear items, which a timing belt usually falls under, unless there is a defect associated with it.
- Manufacturer’s Warranty: Under typical conditions, if the timing belt fails due to a defect in materials or craftsmanship within the specified warranty period, the manufacturer may cover the repair or replacement costs. However, wear-and-tear from regular use, which is a common scenario for timing belts, may not be covered.
- Extended Warranties: If you purchased an extended warranty from a third-party provider or through the dealership, coverage varies widely. Some extended warranties might specifically cover timing belts, while others may only cover related engine components. Always read the fine print and clarify with your warranty provider about the terms.
- Maintenance Responsibilities: If you fail to adhere to the maintenance schedule recommended by the manufacturer, you might find that warranty coverage on your timing belt is voided. Regular maintenance can include inspections and timely replacements to ensure that your vehicle runs smoothly.
What Causes Timing Belt Failure?
Understanding the common causes of timing belt failure can help you take proactive measures to safeguard your vehicle and potentially avoid out-of-pocket expenses if the timing belt needs to be replaced.
- Wear and Tear: Like other components in your vehicle, timing belts deteriorate over time due to heat, friction, and exposure to oil and contaminants. Over time, cracks and frays can develop in the belt material, leading to eventual failure.
- Tensioner Issues: Timing belts work under high tension to function correctly. If the tensioner, which keeps the timing belt tight, malfunctions, it can lead to the belt becoming loose or overly tight. This imbalance can accelerate wear and tear and lead to failure.
- Debris and Contamination: If debris gets into the timing belt area or if coolant leaks onto the belt, it can cause premature deterioration. Ensuring that your engine is in good working order and maintaining cleanliness can protect your timing belt and keep it from failing prematurely.
What Happens When a Timing Belt Fails?
When a timing belt fails, the consequences can be dire. If the timing belt breaks while the engine is running, it can lead to significant and often costly damage.
- Interference vs. Non-Interference Engines: The impact of a failed timing belt depends on whether your vehicle’s engine is an interference or non-interference type. In an interference engine, the valves can collide with the pistons when timing is off, resulting in severe engine damage. In contrast, a non-interference engine typically has a design that allows for a belt failure without catastrophic damage.
- Symptoms of Failure: Before a belt fully fails, there are often warning signs. This includes unusual noises like rattling or grinding, engine misfires, or a check engine light. If you notice these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a mechanic immediately to avoid more significant issues.
Preventive Measures
To prevent unexpected timing belt failure, there are several preventive measures you can take.
- Regular Maintenance Checks: Adhering to your vehicle’s maintenance schedule includes regular inspections of the timing belt. Mechanics will look for visible signs of wear and check for proper tension.
- Timely Replacements: Be proactive and replace your timing belt according to your manufacturer’s recommendations. Waiting until it begins to show wear can be a gamble that may lead to expensive engine repairs.
- Listen to Your Vehicle: Be aware of any unusual noises or performance issues your vehicle may exhibit. When in doubt, have a professional check it out to mitigate potential issues early on.
Conclusion
In summary, a timing belt is a critical component of your vehicle’s engine, and its warranty coverage can vary depending on the type of warranty you have. While a manufacturer’s warranty may cover defects, regular wear-and-tear may not be included. Understanding how your warranty works, adhering to maintenance schedules, and being aware of potential issues can help prevent costly repairs. Always consult your warranty provider or a qualified mechanic for specific information regarding your vehicle’s timing belt.
FAQs
1. How can I determine if my timing belt needs replacement?
Most manufacturers provide a mileage or age recommendation for timing belt replacement. Additionally, if you notice symptoms like unusual noises or engine misfires, it’s a good idea to consult a mechanic.
2. What are the signs that my vehicle’s timing belt is failing?
Common signs include unusual noises, engine misfires, and the check engine light illuminating. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s wise to seek a professional evaluation.
3. Are there alternatives to timing belts?
Some vehicles use timing chains instead of belts. Timing chains typically last longer than timing belts and do not require regular replacement, but they can also fail if not properly maintained.
4. Can I DIY a timing belt replacement?
While experienced DIY mechanics may attempt to replace a timing belt themselves, it’s a complex task that requires specific tools and knowledge. For most car owners, it’s advisable to have a professional handle the replacement to avoid mistakes that could lead to engine damage.
5. What should I do if my timing belt breaks?
If your timing belt breaks while driving, safely pull over to the side of the road and turn off the engine. Do not attempt to drive further, as this can cause severe damage. Contact a towing service to get your vehicle to a mechanic for an assessment and repair.